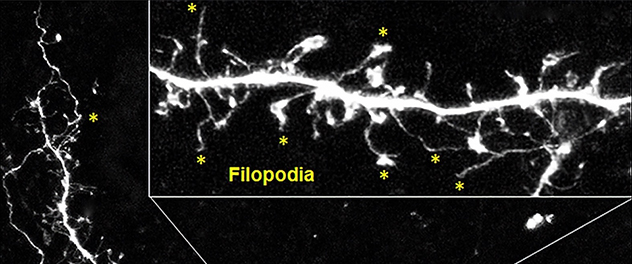
 Fliopodia
Fliopodia
Extensive filopodia formation was observed in the prefrontal cortex layer V neurons of the brains of maternal immune-activated mouse offspring.
Altered microglial function with augmented neuritogenic factor by maternal immune activation
Maternal immune activation disrupts the central innate immune system during a critical neurodevelopmental period. Microglia are primary innate immune cells in the brain, although how maternal immune activation impacts microglial phenotype and function in offspring is largely unknown.
The Molecular Neurotherapeutics lab team led by Dr. Seiko Ikezu demonstrated that maternal immune insults perturb microglial phenotypes and influence neuronal functions throughout adulthood. They also reveal a potent effect of colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibitors on the correction of MIA-associated microglial, synaptic and neurobehavioral dysfunctions. Particularly, Dr. Seiko Ikezu's team has shown that maternal immune activation alters microglial phenotype with upregulation of cellular neuritogenic pathways and downregulation of disease-associated, microglia-related gene expression.
At the same time, maternal immune activation causes repetitive behavior, social deficits and synaptic dysfunction to layer V, intrinsically bursting pyramidal neurons in the prefrontal cortex of mice. Dr. Seiko Ikezu's team also identified that microglia secrete Wnt5a, which has been identified as one of the upregulated molecules in maternal immune activation microglia. Wnt5a regulates the turnover of dendritic spines in primary cultured neurons.
Dr. Seiko Ikezu and her team are investigating whether maternal immune perturbation can change microglial response to the neurodegenerative environment in adult offspring.
References
- Yeh H, Woodbury ME, Ingraham Dixie KL, Ikezu T, Ikezu S. Microglial WNT5A supports dendritic spines maturation and neuronal firing. Brain, Behavior and Immunity. 2023; doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2022.11.003.
- Ikezu S, Yeh H, Delpech JC, Woodbury ME, Van Enoo AA, Ruan Z, Sivakumaran S, You Y, Holland C, Guillamon-Vivancos T, Yoshii-Kitahara A, Botros MB, Madore C, Chao PH, Desani A, Manimaran S, Kalavai SV, Johnson WE, Butovsky O, Medalla M, Luebke JI, Ikezu T. Inhibition of colony stimulating factor 1 receptor corrects maternal inflammation-induced microglial and synaptic dysfunction and behavioral abnormalities. Molecular Psychiatry. 2021; doi:10.1038/s41380-020-0671-2.
Learn more
Learn more about our work.